Launching and Implementing the National Cybersecurity Strategy
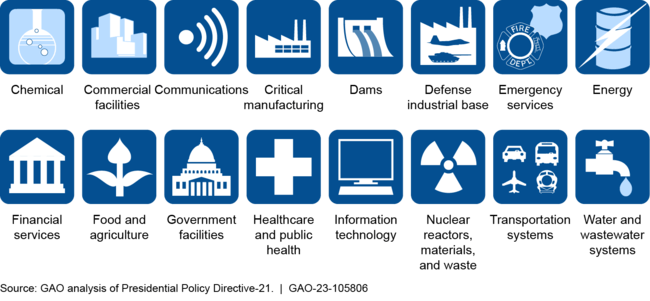
Federal agency information systems and national critical infrastructure are vulnerable to cyberattacks.
The fiscal year 2021 national defense authorization act established the Office of the National Cyber Director (ONCD) and the Senate confirmed a National Cyber Director in June 2021 to serve as the principal advisor to the President on cybersecurity policy and strategy. In March 2023, the White House issued the National Cybersecurity Strategy, describing five pillars supporting the nation's cybersecurity:
- Defend critical infrastructure
- Disrupt and dismantle threat actors
- Shape market forces to drive security and resilience
- Invest in a resilient future
- Forge international partnerships
In April 2023, GAO reported that the goals and strategic objectives included in the document provide a good foundation for establishing a more comprehensive strategy. Specifically, the strategy fully addressed three of six desirable characteristics of a national strategy. However, it only partially addressed the remaining three. These include
- goals, subordinate objectives, activities, and performance measures;
- resources, investments, and risk management; and
- organizational roles, responsibilities, and coordination.
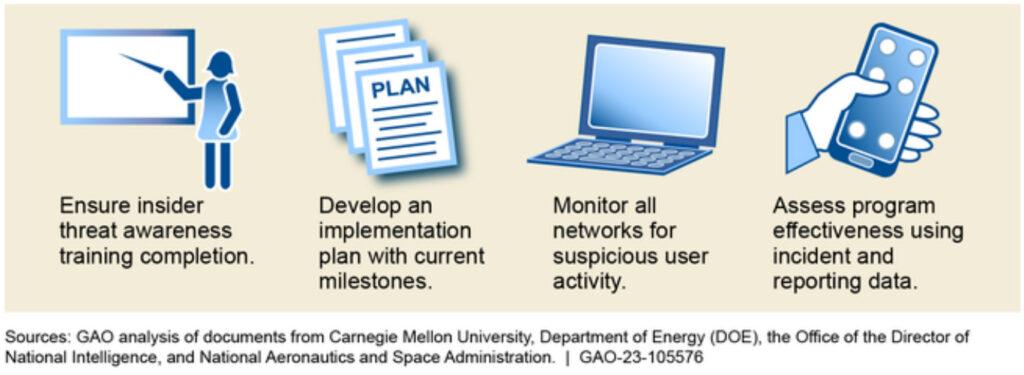
ONCD stated it plans to work with federal agencies to develop a plan to implement the strategy, including milestones or performance measures, and to identify budget priorities. It is critical that these details be issued expeditiously so agencies can begin planning and allocating resources to properly execute the strategy. Until the federal government issues the implementation plan and ensures its strategy documents fully address the desirable characteristics of a national strategy, the nation will lack a clear roadmap for overcoming its cyber challenges.
Additionally, the newly established National Cyber Director position has been vacant since the Director resigned in February 2023. As of July 2023, an acting official continues to carry out the duties. This vacancy leaves unfilled a key leadership role needed to coordinate federal efforts to address cybersecurity threats and challenges. Further, sustained leadership in this position is essential to ensuring strategy execution and accountability.
Why GAO Did This Study
Federal agencies and our nation's critical infrastructure—such as energy, transportation, communications, and financial services—rely on information systems to carry out fundamental operations. Because of the increasing threats to federal information systems, critical infrastructure, and the privacy of personally identifiable information, GAO has designated ensuring the nation's cybersecurity as a government-wide high risk issue. This designation emphasizes the urgency with which the federal government needs to undertake efforts to address the nation's cybersecurity challenges. Accordingly, Congress established the Office of the National Cyber Director in the White House with the authority to implement and encourage action in support of the nation's cybersecurity. One of this office's responsibilities is developing and implementing a comprehensive national strategy to address cybersecurity threats and challenges. This product summarizes recent GAO reports that assessed the federal government's efforts to establish a national cybersecurity strategy and plans for implementing it.
This Snapshot covers the status of the National Cybersecurity Strategy. The strategy's goals and strategic objectives provide a good foundation, but the Administration needs to establish specific objectives and performance measures, resource requirements, and roles and responsibilities.
It will be difficult to implement the strategy when the specific details have yet to be issued. The continued vacancy in the role of National Cyber Director is also a challenge.